Investments for the future
- Equipex Robotex (2011–2020)
- Labex MS2T (2011–2022)
- Equipex+TIRREX (2021–2029)
- Equipex+CONTINUUM (2021–2029)
Equipex Robotex (2011–2020)
Context
Equipex Robotex : 2011–2020
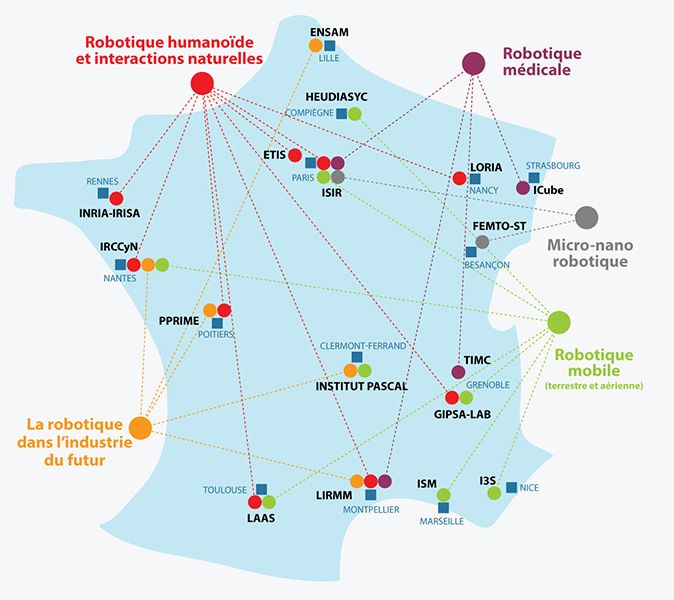
The Equipex Robotex « equipment of excellence » is a network of experimental robotics platforms that extends across 15 laboratories in France, under the stewardship of CNRS.
Within this network, Heudiasyc is in charge of the « Terrestrial and Aerial Mobile Robotics » node (coordinator: Philippe Bonnifait).
Equipments
Robotex has enabled the Lab to acquire and equip the following with high-quality instrumentation:
- 3 robotized electric vehicles (two Renault Zoës and a Renault Fluence)
- A collection of 4‑rotor and 8‑rotor mini-UAVs
- Associated equipment: indoor and outdoor flying arenas, a Renault Master utility vehicle, a 3D printer, high-end sensors, etc.
This equipment has been used to test and validate numerous research works by different teams in the Lab.
The budget allocated to Heudiasyc by Robotex for the 2011–2016 period was € 945k, in addition to € 900k of co-funding by the Picardie (now Hauts-de-France) regional authority and the European Regional Development Fund.
Robotex actions
- In May 2016 Heudiasyc was the only French team to take part in the European Grand Cooperative Driving Challenge GCDC’2016, where ten teams competed against each other in a full-scale demonstration of cooperative autonomous driving. The setting was the A270 motorway between Helmond and Eindhoven in the Netherlands.
- Heudiasyc hosted the Robotex « Techdays » technical seminars in July 2015
Labex MS2T (2011–2022)
Overview
The laboratory of Excellence Labex MS2T was chosen by the French government in March 2011 after being selected by an international jury as part of the « Investments for the Future » program. It received a 6.7 million euros grant for nine years.
The « Laboratories of Excellence » program, coordinated by ANR (french national research agency), aims to provide the best national laboratories with international visibility and significant resources in order to enable them to compete with their foreign counterparts, attract internationally renowned researchers and academics, and create a high-level and integrated policy for research, training and development.
The Labex MS2T “Control of Technological Systems-of-Systems” is a multi-disciplinary scientific problem that targets a scope of application that may be very large.
It brings together 4 laboratories of Compiègne University of Technology associated with CNRS:
- Heudiasyc (leader) : Sciences de l’information et du numérique
- BMBI : Biomécanique, ingénierie de la Santé
- Roberval : Mécanique, Matériaux, Acoustique
Aims and research topics
Labex MS2T will make significant progress on three significant social issues : Transport and Mobility, Security, Health (ICT and Health Engineering).
Topics research
- Interaction and cooperation between systems
- Uncertainty management
- Optimized design of technological SoS
- Dynamics of systems of systems : emergence and agility
Challenge teams
- DIVINA : DIstributed cooperative VIsual Navigation for multi-uAv systems
- DAPAD : Distributed and augmented vehicle perception to support autonomous driving
- INTERFACE : Tissues and cell Interfaces in muscle-skeleton system: Application to the design of bioartificial SoS
Equipex+TIRREX (2021–2029)
Context
The Heudiasyc research laboratory at UTC is involved in the Future Investment Program, « Structuring Equipment for Research » (ESR) Equipex + TIRREX, led by the CNRS.
TIRREX : Technological Infrastructure for Robotics Research of Excellence
Research objectives and focus areas
Objectives
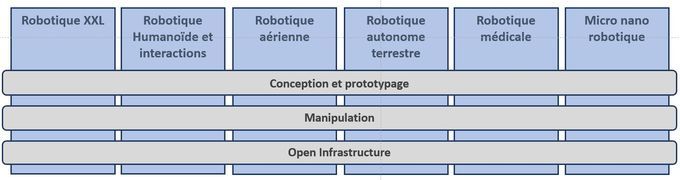
TIRREX (Technological Infrastructure for Robotics Research of Excellence) is the result of several years of research and reflection in the field of robotics. It aims to develop new flagship robotics platforms with national coordination for their access and development.
The project brings together all major actors in French academic robotics research (CNRS, INRIA, CEA, INRAE) and is structured around 6 thematic axes and 3 transversal axes designed to support the thematic axes. Bringing openness to an unprecedented level in robotics, a third transversal axis will focus on open infrastructure.
It aims to ensure, standardize access, and maintain the openness of data, software, and publications produced (FAIR data and open-source software).
Research topics
Equipex+CONTINUUM (2021–2029)
Context
The Heudiasyc research laboratory at UTC is involved in the Future Investment Program, Structuring Equipment for Research (ESR) Equipex + CONTINUUM, led by the CNRS.
CONTINUUM : Collaborative continuum from digital to human
CONTINUUM aims to create a collaborative research infrastructure of 30 platforms located throughout France to advance interdisciplinary research between computer science and the humanities and social sciences.
Research objectives and focus areas
Objectives
Through CONTINUUM, 37 research teams will develop cutting-edge research focused on visualization, immersion, interaction, and collaboration, as well as on human perception, cognition, and behavior in virtual/augmented reality.
CONTINUUM enables a paradigm shift in our perception, interaction, and collaboration with complex digital data and digital worlds by placing the human being at the center of data processing flows.
The project provides scientists, engineers, and industrial users with a network of high-performance visualization and immersion platforms to observe, manipulate, understand, and share digital data, multi-scale simulations, and virtual or augmented experiences. All platforms will enable remote collaboration and will be equipped with mobile devices that can be loaned to users to facilitate access to these technologies.
Research topics
The CONTINUUM project revolves around 2 research axes:
- Interdisciplinary research on interaction, in collaboration between computer science and the humanities and social sciences, to increase knowledge and solutions in human-centered computing;
- Deployment of tools and services to meet the needs of various scientific domains in terms of access to big data, simulations, and virtual/augmented experiences (mathematics, physics, biology, engineering, computer science, medicine, psychology, education, history, archaeology, sociology, etc.).



